When it comes to sealing industrial fabrics, the choice of technology is critical. Two of the most widely used welding processes for fabric sealing are hot air welding and radio frequency (RF) welding, also known as dielectric welding. Both techniques offer unique advantages depending on the material and end-use application. For manufacturers, engineers, and operations managers, understanding the key differences between these technologies can directly impact product quality, production efficiency, and long-term durability.
In this comprehensive comparison guide on hot air vs RF welding, we break down the pros, cons, and ideal use cases for each method. Hot air welding and radio frequency (RF) welding are among several other welding methods available for industrial fabrics, each with its own strengths and applications. Whether you’re producing tents, inflatables, banners, or medical bladders, you’ll gain the clarity needed to choose the right welding method. To learn more about hot air welding specifically, visit our Hot Air Welding Technology Page.
Contact Miller Weldmaster to discuss how we can support your next project involving fabric welding.
What Is Hot Air Welding?
Hot air welding is a thermoplastic welding process that employs a concentrated stream of heated air to soften the surfaces of materials before they are pressed together to create a bond. This process involves heating the surface of the materials, allowing them to fuse when pressed. Hot air welding is a form of heat sealing that uses external heat to bond the material surfaces. This method is well-suited for joining coated textiles and thermoplastic materials such as polyethylene (PE), polyurethane (PU), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) along with many other fabrics. Once heated, the materials are pressed together using rollers to form a consistent, durable seam.
A typical hot air welding setup consists of a heating element, nozzle, pressure rollers, and a control panel for regulating the temperature, pressure, and speed. This enables the operator to fine-tune the process for different fabric types and thicknesses. Hot wedge welding is another related technology for fabric welding, using a heated wedge to bond materials. Hot air welding is particularly advantageous for applications that require continuous seam welding, such as the production of tarps, tents, awnings, and banners.
Advantages of Hot Air Welding
Hot air welding is widely appreciated for its cost-efficiency, making it an accessible option for many standard welding jobs. The equipment used in this process is generally portable, allowing it to be deployed in field settings, such as on construction sites or during on-site repairs. The continuous nature of hot air welding makes it especially beneficial for long seams and high-throughput operations, and is well-suited for high volume production environments. Additionally, hot air welding machines are compatible with a wide variety of thermoplastics, offering versatility across multiple industries.
When to Use Hot Air Welding
Hot air welding is particularly useful for projects that involve long seams on thin to medium-gauge materials. For example, manufacturers of textile products, tents, and banners often rely on hot air welding for its speed and efficiency. This method is ideal in scenarios where field setup is required, and where flexibility and rapid deployment are necessary. Because it accommodates coated fabrics and allows for easy transportation of machinery, hot air welding is often the go-to option for outdoor or on-demand fabrication needs.
Impulse welding is another alternative for light industrial applications, such as window shades, but it may not be suitable for thicker or more complex materials where stronger, more versatile seams are required.

What Is RF Welding?
Radio frequency (RF) welding, also known as dielectric welding, is a fabric sealing method that uses high-frequency electromagnetic energy to generate heat within the material itself. Dielectric sealing is another term for this process. The development of radio frequency technology in the mid-20th century revolutionized industrial fabric sealing by enabling more precise and durable bonds. In RF welding, high frequency energy is used to create an electromagnetic field between two electrodes. RF energy causes the polar molecules in the thermoplastic material to oscillate, generating heat internally. This process allows the material to soften and fuse from the inside out. Welding is the process of bonding materials by internally heating them using RF energy, resulting in strong, uniform seams.
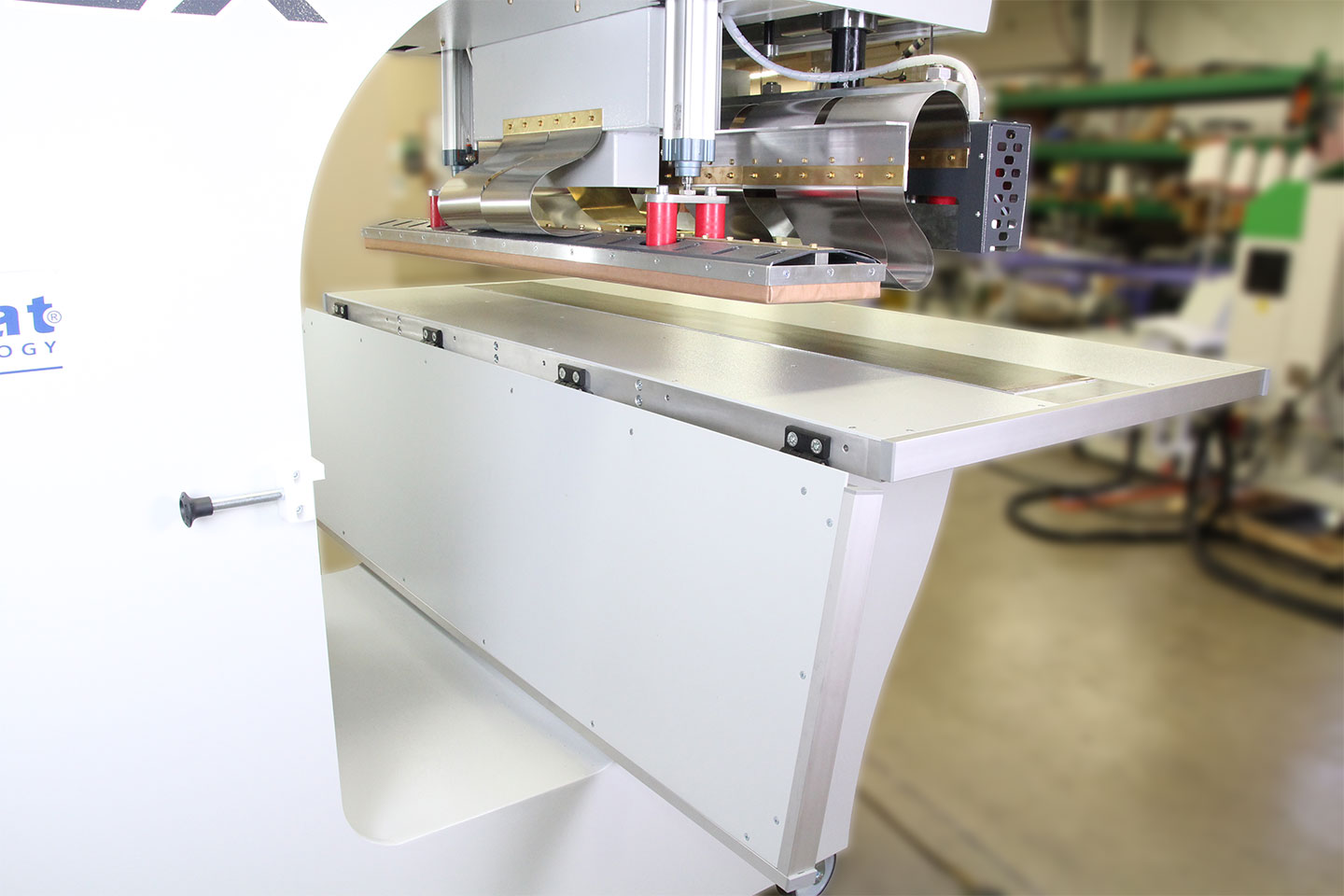
RF welding is particularly effective for homogeneous thermoplastic materials, most notably PVC and TPU. RF welding heats the material from the inside, and this internal heating heats the material uniformly, enabling the fusion of thicker or coated plastics that are difficult to join with surface heating methods. Because it generates hermetically sealed bonds, RF welding is the preferred choice for applications that require airtight or waterproof seams, such as medical products, inflatables, fluid bladders, and protective gear. Welding time is a critical parameter for achieving strong, consistent bonds during the process. For a more detailed look at the technology, visit our RF Welding Technology Page.
Advantages of RF Welding
One of the standout benefits of RF welding is its ability to create airtight and watertight seams, creating strong and durable bonds. The process forms a weld seam that is both strong and reliable. RF welding produces a permanent seam that is resistant to environmental factors, and the strength of the seam can be as great as or greater than the surrounding material. This level of seal integrity is difficult to achieve with other methods. Additionally, RF welding provides a high degree of precision, ensuring uniform results across production batches. The welds produced through RF welding are typically long-lasting, smooth, and aesthetically clean. These characteristics make RF welding a popular choice in industries where reliability and presentation are equally important, such as medical device manufacturing and high-end inflatables.
When to Use RF Welding
RF welding is the method of choice when absolute air or water-tightness is non-negotiable. This includes applications like inflatable boats, inflatable products, oil booms, medical fluid bags, and safety equipment used in aerospace. It is also well-suited for thick or multilayer PVC products where a consistent bond is essential. For medical products, such as medical devices and RF welded products, RF welding provides the reliable, sterile, and durable seals required. Due to the control and precision it offers, RF welding is often used in environments with strict regulatory or quality requirements.

Hot Air vs RF Welding: Key Differences Explained
Selecting the best method for welding or sealing materials depends on several important factors, such as material type, seam strength, and production requirements. The table below compares hot air welding and RF welding to help you determine which is the best method for your application.
| Feature | Hot Air Welding | RF Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | External hot air | Internal RF electromagnetic energy |
| Material Compatibility | Wide range of coated thermoplastics | Homogeneous thermoplastics (PVC, TPU) |
| Seam Strength | Strong, but less than RF for airtight | Extremely strong and airtight |
| Equipment | Portable, lower cost | Larger footprint, more precise |
| Setup & Training | Easier to set up and use | Requires more training and calibration |
| Cost | Lower capital and maintenance cost | Higher initial investment |
Materials and Fabric Compatibility
Hot air welding is adaptable to a wide range of materials, including coated fabrics like polyethylene, polyurethane, and vinyl. It performs well on laminated textiles and thin to medium-gauge thermoplastics. Material thickness and overall thickness are critical factors in determining the suitability of each welding method, as they can significantly impact weld strength and quality. Conversely, RF welding is best used on homogeneous thermoplastics, particularly PVC and TPU, due to their ability to respond to electromagnetic energy. When working with non-homogeneous or coated materials, RF welding may not be effective or feasible.
Durability and Strength of Seams
In terms of seam strength and durability, RF welding generally outperforms hot air welding, especially in applications that require airtight or fluid-tight seals. RF-welded seams are known for their resistance to stretching, puncturing, and environmental degradation. While hot air welding also produces robust seams, it may not meet the stringent performance standards required in high-pressure or critical containment applications.
Equipment and Operational Considerations
Hot air welding equipment is typically more compact and portable, making it easier to transport and use in field settings. This can be a significant advantage for businesses that require on-site fabrication or frequent equipment relocation. RF welding equipment, by contrast, usually has a larger footprint and is designed for stationary, high-precision production environments. RF welding systems are also well-suited for high volume production environments, accommodating large-scale manufacturing needs. While RF systems offer superior control and consistency, they also demand more extensive operator training and maintenance.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Product
Determining whether to use hot air or RF welding for your application involves evaluating several key factors:
The intended function of the product plays a crucial role. Depending on the size, shape, and need of the product, you will need to decide which technology is best for you. Both offeruniqueoptions
The type of fabric you’re working with also matters. Homogeneous thermoplastics like PVC and TPU are ideal candidates for RF welding, whereas coated fabrics are typically better suited to hot air methods. RF welding is particularly effective for joining multiple layers or two layers of thermoplastic material, while hot air welding may be better for a single layer or coated fabrics. The ability to weld several layers at once can be a deciding factor, especially for complex or multi-layered products.
Why Manufacturers Trust Miller Weldmaster for Fabric Welding
For over 50 years, Miller Weldmaster has been a trusted name in the industrial fabric welding industry. Our experience spans a wide array of sealing technologies, from hot air to radio frequency, and we understand the challenges manufacturers face when choosing the best solution for their production needs. We have extensive expertise in welding work for a variety of industrial applications, ensuring durable, precise, and versatile welds using advanced RF welding techniques.
We provide a diverse range of fabric welding systems tailored to specific industry applications. Our team of engineers and support specialists work closely with customers to develop customized solutions that align with performance goals and material requirements. Miller Weldmaster is not just a machine provider—we are a strategic partner dedicated to your success.
Explore Miller Weldmaster Machines Built for Precision Sealing
At Miller Weldmaster, we design our machines to meet the precise requirements of modern manufacturing. Our lineup includes both hot air and RF welding machines, each optimized for specific use cases.
The T300 Extreme Curve is a powerful hot air welding machine engineered for curved and complex seams. It’s widely used in the production of inflatables, tanks, and other custom-shaped products.
The RFlex is our flagship RF welding system. It is built for precision and durability, making it ideal for manufacturers of air-tight and liquid-tight products such as medical bags and inflatable equipment.
With each machine, we offer comprehensive training, installation, and ongoing support to ensure your team can operate efficiently and effectively. Miller Weldmaster's machines allow for strong, durable bonds without the use of adhesives.
Ready to explore the best welding method for your products? Reach out to the experts at Miller Weldmaster or browse our technologies to discover the perfect fit.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hot Air vs RF Welding
What’s the difference between hot air and RF welding?
Hot air welding uses an external heat source to melt fabric surfaces before pressing them together. RF welding generates heat internally by using electromagnetic energy to vibrate molecules, allowing for more uniform bonding. RF typically produces stronger, more airtight seams.
Which fabrics are best for RF welding?
RF welding works best with homogeneous thermoplastic materials such as PVC and TPU. These materials respond well to the electromagnetic frequencies used in RF welding.
Is hot air welding waterproof?
Yes, hot air welding can create waterproof seams when executed properly. However, the level of waterproofing may vary depending on the material and seam design, and it may not meet the same standards as RF-welded seams in critical applications.
When should I choose RF welding over hot air welding?
RF welding is preferable when the application requires airtight or watertight seals, such as in inflatables, medical fluid containers, or high-performance protective gear.
What are the limitations of hot air welding?
Hot air welding may struggle to create airtight seams on thick or multilayered materials. It may also be less suitable for precision bonding in regulated industries such as medical or aerospace.
Can I use RF welding on coated fabrics?
Generally, RF welding is not effective on coated fabrics because the coating can interfere with the transmission of electromagnetic energy. Hot air welding is usually the better choice for coated textiles.
Which method is more cost-effective for large-scale production?
Hot air welding is generally more cost-effective due to lower equipment costs and easier setup. However, RF welding may provide better long-term value for applications that require high reliability and minimal rework.
Are RF welding machines harder to operate than hot air welders?
RF welding machines require more operator training and calibration due to their complexity. However, once mastered, they provide unmatched precision and repeatability.
How long do welded seams last?
Seam longevity depends on the material and application, but both hot air and RF welded seams can last for years or even decades if properly maintained.
Does Miller Weldmaster provide support for both methods?
Yes. Miller Weldmaster offers machines, training, and support for both hot air and RF welding methods, ensuring that manufacturers have the resources they need to succeed.



.png)