Hot air welding machines represent precision engineering at its finest, delivering controlled heat between 700°F to 1,350°F (400°C to 730°C) to create molecular-level bonds in thermoplastic materials. Unlike traditional adhesive methods, these sophisticated plastic welding tools generate seamless, waterproof joints that often exceed the strength of the parent material itself.
Whether you’re installing commercial roofing systems, welding vinyl flooring, or fabricating automotive components, understanding the capabilities and applications of hot air technology can transform your project efficiency and results. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about selecting, operating, and maximizing the potential of hot air welding equipment for your specific applications.
What Are Hot Air Welding Machines
Hot air welding machines are specialized plastic welding equipment designed to join thermoplastic materials through a precise heating and pressure process. The welding process works by directing superheated, compressed air through engineered nozzles onto the joint interface between thermoplastic layers. This controlled heat application softens the material surfaces, allowing pressure rollers or manual force to create a homogeneous molecular bond as the material cools.
The core components of these machines include:
- Electrically powered heating elements that raise air temperature to exact specifications
- Precision nozzles that focus heated air streams onto welding areas
- Pressure application systems including rollers for consistent bonding force
- Digital or analog controls for temperature, airflow, and speed management
- Motor and drive systems in automatic welders for uniform seam creation
What sets hot air welding apart from other joining methods is its ability to create true molecular bonds rather than surface adhesion. This process eliminates the need for consumables like adhesives or mechanical fasteners, while producing seams that maintain the original material properties. The technology proves essential for applications requiring waterproof, chemical-resistant, and structurally sound joints across many applications in industrial settings.
Types of Hot Air Welding Equipment
The diversity of hot air welding machines reflects the varied demands of modern industrial applications. Understanding each type helps ensure you select equipment that matches your production requirements and project constraints.
Hand-held Hot Air Welding Torches
Manual welding tools offer maximum flexibility for detail work, repairs, and applications requiring operator precision. These ergonomic design units typically weigh between 2-4 pounds and feature variable temperature and airflow controls. Heat guns in this category excel at field repairs, complex geometries, and situations where access is limited. The portable nature of handheld welders makes them indispensable for on-site work where efficiency and mobility matter.
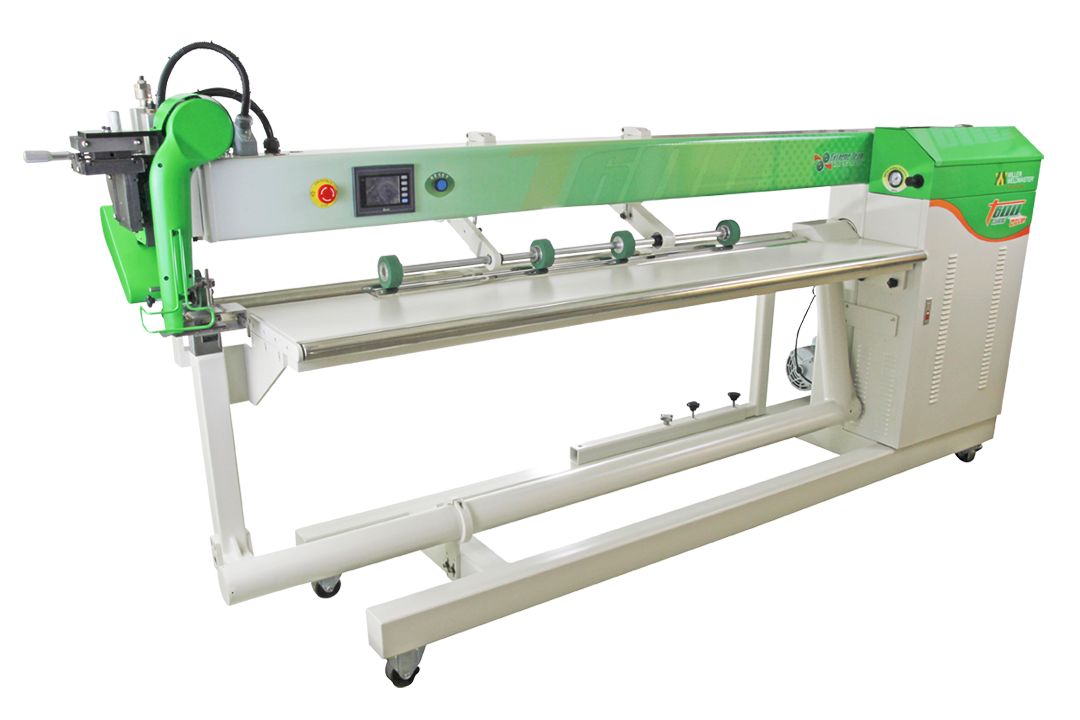
Semi-Automatic Welding Machines
Semi-automatic welders bridge the gap between manual control and full automation. These machines combine motorized movement with operator oversight, providing consistent speed and temperature while allowing real-time adjustments. This category proves ideal for medium-volume production where flexibility remains important but consistency needs improvement over purely manual methods.
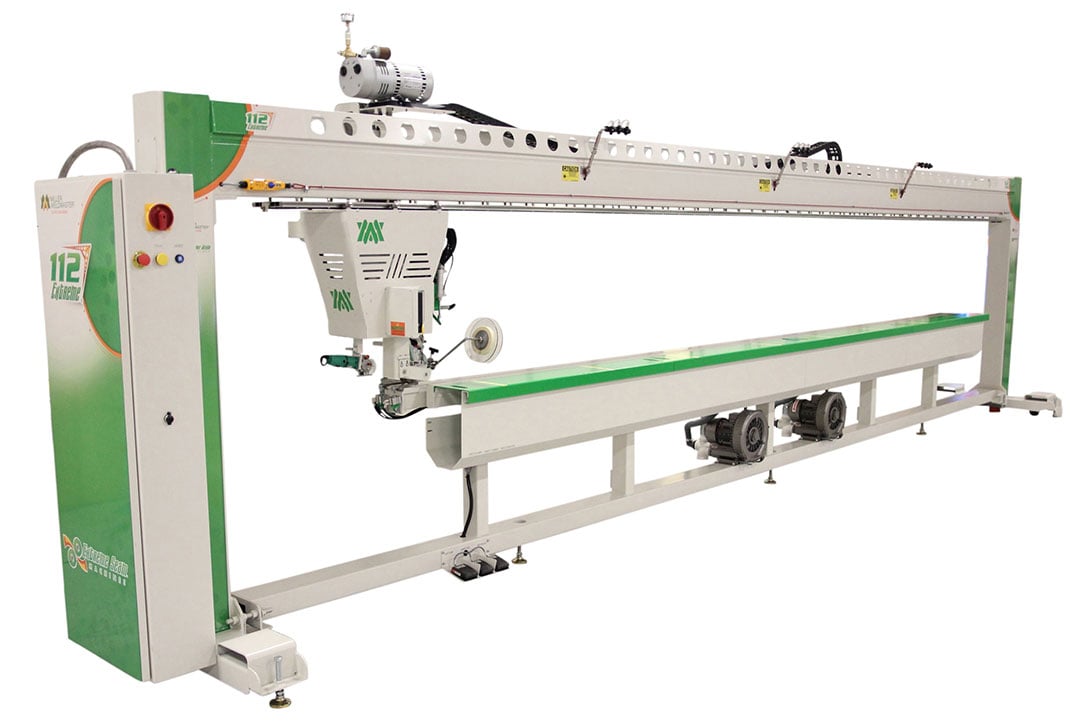
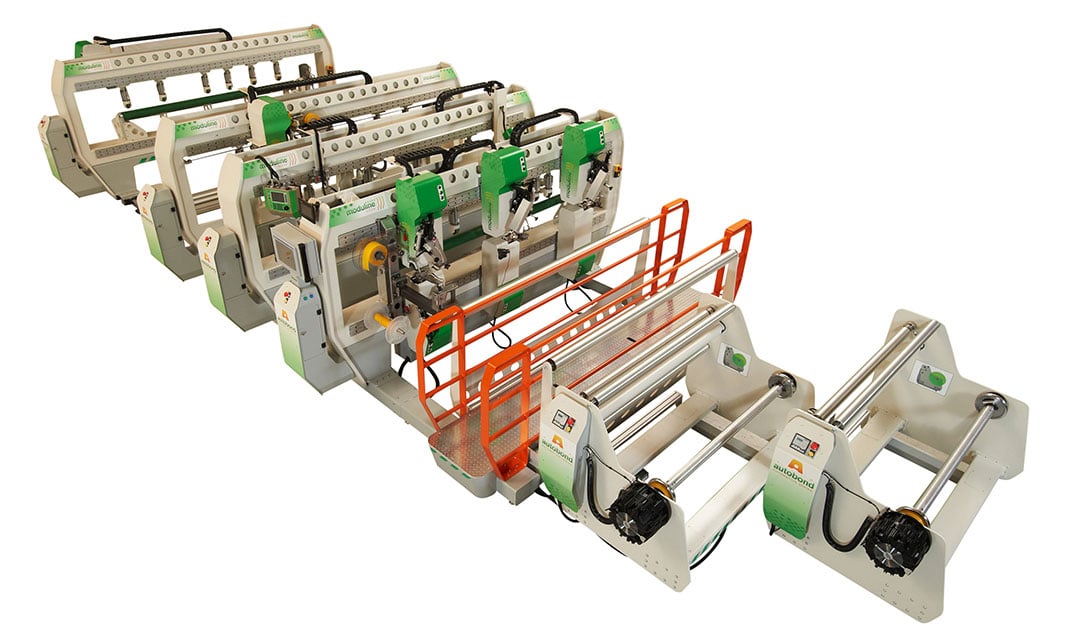
Automatic Welders
Fully automatic welding machines represent the pinnacle of production efficiency for high-volume operations. These sophisticated systems integrate programmable controls, robotic material guides, and feedback sensors for temperature and seam alignment. Automatic welders reduce operator error, dramatically increase speed, and deliver superior seam consistency—critical factors for mass manufacturing environments.
Specialized Roof Welding Equipment
Roof welder machines are purpose-built for installing TPO (thermoplastic polyolefin) and PVC membrane systems. These rugged units withstand outdoor conditions while maintaining precise weld quality across variable surface conditions. Professional roof welding equipment often features enhanced portability, weather-resistant controls, and specialized nozzles optimized for membrane materials.
Popular Hot Air Welding Machine Models
The market offers several standout models that have earned industry recognition:
- Duratherm2 and Autotherm3 torches feature integrated electronic temperature controls and precise airflow management, making them ideal for delicate materials requiring exact heat application
- Exotherm and Airtherm2 models include self-contained air supply systems, eliminating the need for external compressors and maximizing portability for remote job sites
- RoofOn series and LarOn 21 welders represent professional-grade automatic machines favored for their high-speed operation and sophisticated seam tracking capabilities
- SolOn floor welding machines specialize in vinyl and resilient flooring applications, offering digital speed controls and interchangeable nozzle assemblies
Key Applications and Industries
Hot air welding technology serves critical roles across diverse industrial sectors, each demanding specific performance characteristics and reliability standards.
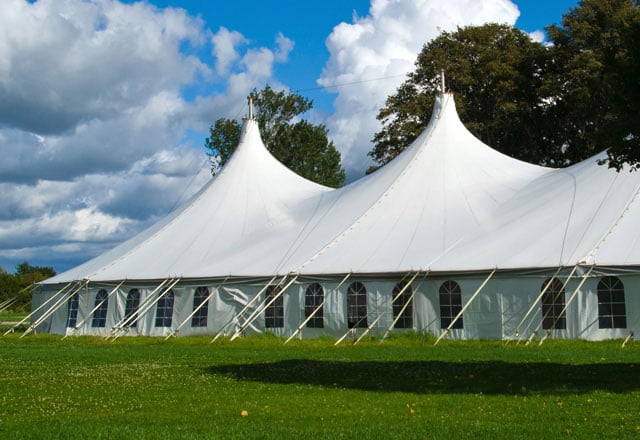
Commercial Roofing Installation
Single-ply membrane roofing systems rely heavily on hot air welding for creating watertight, UV-resistant seams. TPO and PVC membrane installation requires precise temperature control to ensure proper bonding without material degradation. Professional roofers depend on specialized welding machines to achieve consistent seam quality across large roof areas, with weld speeds often determining project timelines and profitability.
Vinyl Flooring Installation and Repair
The flooring industry utilizes hot air welding to create seamless joints between vinyl planks and sheets. This application prevents moisture infiltration and contamination while maintaining aesthetic continuity. Commercial and residential projects benefit from the clean, efficient process that eliminates adhesive odors and reduces installation time compared to traditional methods.
Automotive Interior Manufacturing
Automotive applications showcase the precision capabilities of hot air technology in joining dashboard components, trim pieces, and soft-touch thermoplastic elements. The welding process enables complex geometries and multi-material assemblies while meeting stringent safety and durability requirements. Manufacturing efficiency gains from automated welding systems contribute significantly to production line optimization.
Textile and Industrial Fabric Welding
Technical textiles, awnings, banners, and inflatable products rely on hot air welding for joining PVC-coated and polyurethane fabrics. This application requires careful heat management to avoid fabric damage while ensuring strong, flexible seams. The ability to create waterproof joints makes this technology indispensable for outdoor and marine applications.
Plastic Fabrication and Manufacturing
Industrial plastic fabrication depends on hot air welding for assembling tanks, ducts, machinery housings, and custom components. The process creates leak-proof joints essential for chemical processing, water treatment, and manufacturing equipment. Fabrication shops value the speed and reliability of welded joints over mechanical fastening methods.
Advantages of Hot Air Welding Technology
The technical superiority of hot air welding stems from several key advantages that address common challenges in thermoplastic joining applications.
Precise Temperature and Process Control
Electronic temperature controls with digital displays enable operators to match heat output precisely to material requirements. This precision prevents overheating that can weaken materials or underheating that results in poor bonds. Advanced machines maintain temperature stability within ±5°F, ensuring consistent results across production runs.
Material Versatility and Compatibility
Hot air technology accommodates a broad spectrum of thermoplastic materials including PVC, PE, PP, PU, and TPO. Multi-layered and coated fabrics respond well to controlled heat application, expanding the range of possible applications. This versatility reduces the need for multiple joining technologies in diverse manufacturing environments.
Clean, Consumable-Free Process
The absence of adhesives, solvents, or mechanical fasteners eliminates material costs and potential failure points. Workers benefit from improved air quality since the process produces no volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Environmental considerations favor hot air welding as a green technology that reduces chemical waste and disposal requirements.
Superior Speed and Productivity
Welding speeds significantly exceed those of adhesive curing or mechanical fastening methods. Automatic welders can achieve linear speeds of 15-25 feet per minute on suitable materials, dramatically reducing production time. The immediate bond formation eliminates waiting periods required for adhesive curing.
Structural Integrity and Performance
Welded seams often match or exceed the strength of parent materials, creating homogeneous joints without weak points. Waterproof characteristics prove essential for roofing, containment, and marine applications. The molecular bonding ensures long-term performance under stress, temperature cycling, and environmental exposure.
Essential Features to Consider
Selecting optimal hot air welding equipment requires careful evaluation of features that directly impact performance, efficiency, and long-term value.
Electronic Temperature Controls
Digital temperature displays and precise control systems ensure repeatable results across different materials and operators. Look for machines offering temperature ranges appropriate for your specific applications, with incremental adjustment capabilities. Advanced controls often include memory settings for storing frequently used parameters.
Adjustable Welding Speed Settings
Variable speed controls accommodate different material thicknesses, seam geometries, and production requirements. Semi-automatic and automatic machines benefit from programmable speed settings that ensure consistent results. Consider machines offering both fine and coarse speed adjustments for maximum flexibility.
Self-Contained Air Supply Systems
Integrated air supply units provide complete portability, enabling operation in locations without compressed air infrastructure. These systems eliminate setup time and ensure consistent air pressure for optimal welding quality. Evaluate air flow capacity to match your application requirements and duty cycle needs.
Ergonomic Design and Weight Considerations
Handheld units should feature balanced weight distribution and comfortable grips to reduce operator fatigue during extended use. Consider torch design, cable management, and overall machine ergonomics when evaluating equipment for manual applications. Lightweight construction becomes critical for overhead work and extended operation periods.
Nozzle Versatility and Interchangeability
Multiple nozzle options expand machine capabilities across different seam types and welding techniques. Tacking nozzles enable initial positioning, while speed welding tips maximize production rates. Quick-change nozzle systems minimize downtime when switching between application types.
Accessories and Support Equipment
Maximizing the potential of hot air welding machines requires careful selection of accessories and support equipment that enhance productivity and maintain quality standards.
Specialized Welding Nozzles
Different nozzle configurations optimize airflow and heat distribution for specific applications:
- Tacking nozzles provide precise heat for initial seam positioning
- Speed welding tips maximize linear welding rates for production work
- Overlap welding nozzles ensure proper heat distribution across seam widths
- Corner and detail nozzles accommodate complex geometries and tight spaces
External Air Supply Equipment
Machines requiring external air sources benefit from properly sized compressors and air preparation equipment. Consider air volume requirements, pressure specifications, and filtration needs when selecting support equipment. Consistent air quality directly impacts welding performance and equipment longevity.
Measuring and Guide Tools
Seam guides ensure straight, consistent welds while reducing operator skill requirements. Measuring devices help maintain proper overlap distances and seam spacing. These tools become particularly valuable for large-scale installations where accuracy and appearance matter.
Finishing and Maintenance Tools
Cutting knives and bead removal tools enable clean seam finishing and material trimming. Regular maintenance requires replacement heating elements, brush kits, and cleaning supplies. Establishing proper maintenance schedules and having essential parts readily available minimizes downtime and ensures consistent performance.
Choosing the Right Hot Air Welding Machine
The selection process should systematically address your specific requirements, constraints, and growth expectations to ensure optimal equipment investment.
Material Compatibility Assessment
Begin by cataloging the thermoplastic materials and thicknesses you’ll encounter most frequently. Verify that prospective machines offer appropriate temperature ranges, nozzle options, and pressure capabilities for your material palette. Consider future material requirements that might influence equipment selection.
Production Volume Analysis
Evaluate your current and projected production volumes to determine whether manual, semi-automatic, or automatic equipment best serves your needs. High-throughput operations typically justify automatic welders despite higher initial costs, while smaller volumes may favor flexible manual systems.
Workplace and Portability Requirements
Assess your typical work environments to determine portability needs, power requirements, and space constraints. Jobsite work often demands compact, self-contained units, while factory installations can accommodate larger, more sophisticated equipment with external utilities.
Operator Skill and Training Considerations
Consider your team’s current capabilities and training requirements when evaluating equipment complexity. Digital interfaces and automated features can reduce skill requirements and training time while improving consistency. Balance sophistication with operational simplicity based on your workforce capabilities.
Expert Consultation and Support
Given the technical complexity of welding applications, consulting with experienced equipment specialists ensures your investment aligns with operational needs. Reputable suppliers offer application testing, training programs, and ongoing technical support that prove valuable throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Quality suppliers also provide demonstrations, allowing hands-on evaluation before purchase. This opportunity to test equipment with your actual materials and applications reduces selection risk and ensures compatibility.
Conclusion
Hot air welding machines represent sophisticated technology that transforms thermoplastic joining applications across industries. From precision handheld tools for detailed work to high-speed automatic systems for production environments, these machines offer unmatched versatility and performance for creating strong, waterproof, and durable seams.
Success with hot air welding technology depends on understanding your specific application requirements, selecting appropriate equipment features, and establishing proper operational procedures. The investment in quality equipment pays dividends through improved efficiency, superior results, and reduced long-term costs compared to alternative joining methods.
Whether you’re entering the field or upgrading existing capabilities, take time to evaluate your needs thoroughly and consult with welding equipment experts who can guide you toward the optimal solution. The right hot air welding machine will serve as a reliable foundation for years of productive operation and professional results.
Take Your Welding to the Next Level with Miller Weldmaster
At Miller Weldmaster, we pride ourselves on delivering cutting-edge hot air welding machines that combine precision, efficiency, and durability. Whether you need expert advice, customized solutions, or reliable equipment for your plastic welding projects, our team is ready to support you every step of the way. Contact Miller Weldmaster today to speak with our specialists, discover our range of innovative welding technology, and find the perfect machine to enhance your productivity and quality. Let Miller Weldmaster be your trusted partner in achieving welding excellence.
If you do not see your fabric listed here, please contact us and tell us about your fabric welding needs. With our expertise in hot air welding and the use of a suitable hot air welder, we can accommodate diverse industrial hot air welding requirements.